The result will be a present value cash settlement that will be less than the sum total of all the future payments because of discounting (time value of money). An ordinary annuity is a series of equal payments made at the end of consecutive periods over a fixed length of time. This variance in when the payments are made results in different present and future value calculations. Present value is an important concept for annuities because it allows individuals to compare the value of receiving a series of payments in the future to the value of receiving a lump-sum payment today. By calculating the present value of an annuity, individuals can determine whether it is more beneficial for them to receive a lump sum payment or to receive an annuity spread out over a number of years.
Present Value of a Perpetuity (t → ∞) and Continuous Compounding (m → ∞)
If you’re looking for an investment strategy that goes beyond “buy and hold” while controlling risk and requiring as little as 30 minutes a month to manage, this is the answer. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Mortgages and certain notes payable in equal installments are examples of present-value-of-annuity problems. It is important to distinguish between the future value and the present value of an annuity. Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia. “Essentially, a sum of money’s value depends on how long you must wait to use it; the sooner you can use it, the more valuable it is,” Harvard Business School says.
Recommended Finance Resources
All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Another way to interpret this problem is to say that, if you want to earn 8%, it makes no difference whether you keep $13,420.16 today or receive $2,000 a year for 10 years. Again, please note that the one cent difference in these results, $5,801.92 vs. $5,801.91, is due to rounding in the first calculation. Note that the one cent difference in these results, $5,525.64 vs. $5,525.63, is due to rounding in the first calculation. So, let’s assume that you invest $1,000 every year for the next five years, at 5% interest.
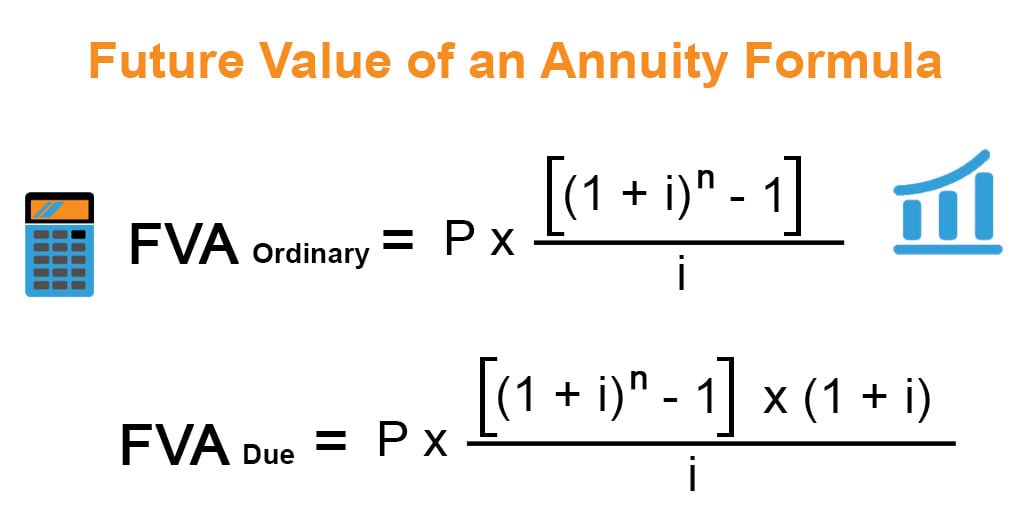
The Annuity Formula for the Present and Future Value of Annuities
If it’s not filled in, please enter the title of the calculator as listed at the top of the page. If you have a question about the calculator’s operation, please enter your question, your first name, and a valid email address. All calculators have been tested to work with the latest Chrome, Firefox, and Safari web browsers (all are free to download). I gave up trying to support other web browsers because they seem to thumb their noses at widely accepted standards.
They also often contain a death benefit in the event you die and are unable to withdraw the money as income at retirement. Have you been preparing for retirement by making regular deposits into an account? First enter the amount of the payment that you’ve been making, the account’s interest rate, the number of years you’ve been making these deposits, and the payment interval.
The growing annuity formula
- There are fixed annuities, where the payments are equal, but also variable annuities, that you allow to accumulate and then invest based on several, tax-deferred options.
- If you read on, you can learn what the annuity definition is, what is the present value of annuity as well as how to use this annuity payment calculator.
- Buying an annuity usually refers to investment plans, for example insurance products, that provide a steady stream of income in retirement.
- The present value of annuity is the current worth or cost of a fixed stream of future payments.
Unless insurance companies go bankrupt, fixed annuities promise the return of principal. As a result, they are commonly used by retirees to guarantee themselves a steady income for the rest of their lives. They also tend to be useful for more conservative investors or people who want a way to control their spending through regulated, steady cash flows. An annuity is a binding agreement between you and an insurance company that aids in meeting your monetary goals at retirement.
On the other hand, the future value of an annuity will be greater than the sum of the individual payments or receipts because interest is accumulated on the payments. Similarly, the formula for calculating the PV of an annuity due takes into account the fact that payments are made at the beginning rather than the end of each period. The reason the values are higher is that payments made at the beginning of the period have more time irs moving expense deductions to earn interest. For example, if the $1,000 was invested on January 1 rather than January 31, it would have an additional month to grow. As mentioned, an annuity due differs from an ordinary annuity in that the annuity due’s payments are made at the beginning, rather than the end, of each period. FV is a measure of how much a series of regular payments will be worth at some point in the future, given a specified interest rate.
That’s because $10,000 today is worth more than $10,000 received over the course of time. In other words, the purchasing power of your money decreases in the future. Suppose that Black Lighting Co. purchased a new printing press for $100,000. The quarterly payments are $4,326.24 and the rate is 12% annually (or 3% per quarter).
Financial calculators also have the ability to calculate these for you, given the correct inputs. These recurring or ongoing payments are technically referred to as annuities (not to be confused with the financial product called an annuity, though the two are related). Because of the time value of money, money received today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future because it can be invested in the meantime. By the same logic, $5,000 received today is worth more than the same amount spread over five annual installments of $1,000 each.
You can notice that for a positive discount rate, the future value (FV – future value calculator) is always higher or equal to the present value (PV). NPV is often used in company valuation – check out the discounted cash flow calculator for more details. This is usually allowable within the first 10 to 30 days of signing the contract.
The present value of an annuity is the present cash value of payments you will receive in the future. The easiest way to understand the difference between these types of annuities is to study a simple case. Let’s presume that you will receive $100 annually for three years, and the interest rate is 5 percent; thus, you have a $100, 3-year, 5% annuity. As long as we know two of the three variables, we can solve for the third.
